Tired of those stubborn dark circles? Discover how nutrition can be your secret weapon for brighter, healthier skin. This comprehensive guide by Dr. Sumaiya’s NutriCare Clinic dives deep into the nutritional strategies to combat dark circles and under-eye pigmentation, offering practical tips and expert advice. Get ready to unlock a radiant complexion from the inside out!
Understanding Dark Circles and Under-Eye Pigmentation
Dark circles and under-eye pigmentation are common cosmetic concerns, affecting people of all ages. They can make you appear tired, stressed, and older than your actual age. While genetics, lack of sleep, and dehydration are well-known contributors, nutrition plays a crucial, often overlooked role. At Dr. Sumaiya’s NutriCare, we address these issues from the inside out, leveraging the power of a balanced diet for healthier, brighter skin.
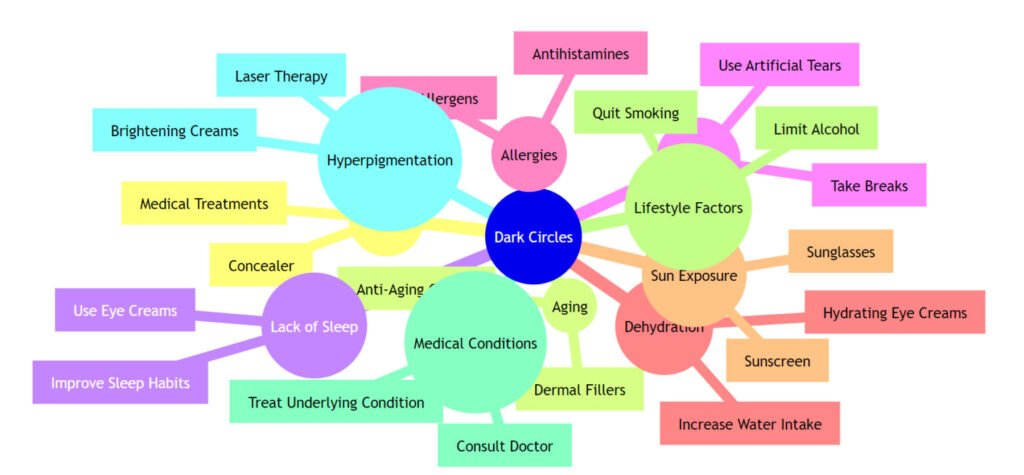
What Causes Dark Circles?
- Thin Skin: The skin under the eyes is exceptionally delicate and thin, making blood vessels more visible.
- Dehydration: Lack of water can cause the skin to appear dull and sunken. Studies, such as those published by the National Institutes of Health, show that even mild dehydration can significantly impact skin appearance and elasticity.
- Fatigue: Poor sleep reduces blood circulation, leading to a pale complexion and a darkened under-eye area.
- Genetics: Family history can predispose you to darker pigmentation around the eyes.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: A lack of iron can reduce oxygen delivery to tissues, making the under-eye area appear darker.
What Causes Under-Eye Pigmentation (Periorbital Hyperpigmentation)?
- Sun Exposure: UV rays stimulate melanin production, leading to darkened skin. The American Academy of Dermatology emphasizes the importance of sun protection in preventing hyperpigmentation.
- Aging: Loss of collagen and fat makes blood vessels more prominent, and the skin becomes thinner.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a poor diet can exacerbate pigmentation.
- Inflammation: Allergies, eczema, and other inflammatory conditions can contribute to hyperpigmentation.
Nutritional Strategies for Reducing Dark Circles and Pigmentation
A well-balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients, is key to combating dark circles and promoting healthy, radiant skin. Here are some crucial nutritional strategies:
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Water helps flush out toxins, supports skin elasticity, and improves circulation. Aim for at least 8 glasses (approximately 2 liters) of water a day. Incorporate hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges into your diet.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis, which maintains skin’s firmness and elasticity. It also possesses potent antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Excellent sources include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Iron
Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, causing pale skin and dark circles due to reduced oxygen supply to tissues. Include lean meats, spinach, lentils, beans, and fortified cereals in your diet.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K plays a role in blood clotting and healing. It can help reduce the visibility of dark circles by improving blood flow and reducing capillary leakage. Good sources include leafy greens (kale, spinach, collard greens), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants combat free radicals that damage skin cells and lead to pigmentation. A diet rich in antioxidants helps maintain a healthy, radiant complexion. Consume berries (blueberries, raspberries, strawberries), nuts (almonds, walnuts), and green tea.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce inflammation and support skin hydration and elasticity. Find them in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits for Under-Eye Area |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli | Collagen synthesis, antioxidant protection |
| Iron | Lean meats, spinach, lentils, fortified cereals | Improves oxygen supply to tissues, reduces paleness |
| Vitamin K | Leafy greens, broccoli, Brussels sprouts | Improves blood flow, reduces capillary leakage |
| Antioxidants | Berries, nuts, green tea | Fights free radicals, promotes radiant complexion |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts | Reduces inflammation, supports skin hydration |
Addressing Anemia-Related Dark Circles
Anemia, particularly iron-deficiency anemia, can cause the skin to become pale and dull due to a lack of adequate red blood cells. This paleness makes the blood vessels under the thin skin around the eyes more visible, creating the appearance of dark circles. Addressing the underlying anemia through diet, supplements (under medical supervision), or medical treatment can significantly improve the appearance of dark circles.
- Dietary Sources of Iron: Lean meats, spinach, lentils, beans, and fortified cereals. It’s important to note that heme iron (from animal sources) is more readily absorbed than non-heme iron (from plant sources). Pairing non-heme iron with Vitamin C-rich foods enhances absorption.
- Iron Supplements: If dietary changes are insufficient, a doctor may recommend iron supplements. *Never* start iron supplements without consulting a healthcare professional, as excessive iron can be harmful.
- Medical Treatment: In some cases, anemia may be caused by an underlying medical condition that requires specific treatment.
For personalized guidance on managing anemia and its impact on your skin, consider a consultation.
Book Your Consultation NowThe Impact of Stress on Dark Circles
Stress contributes to the development of dark circles through several mechanisms:
- Sleep Disruption: Stress often leads to poor sleep quality or insomnia, accentuating dark circles. Lack of sleep reduces blood flow to the skin, making it appear paler and allowing dark tissues and blood vessels beneath the skin to become more visible.
- Skin Health: Stress increases cortisol production, which can lead to thinner skin and more visible blood vessels. Cortisol can also break down collagen, the protein that keeps skin firm and elastic.
- Fatigue: Constant stress causes fatigue, making dark circles more prominent.
- Dehydration and Poor Nutrition: Stress can lead to poor dietary choices and dehydration, further impacting skin health. When stressed, people may neglect to drink enough water or opt for unhealthy comfort foods.
- Eye Strain: Increased screen time and eye strain from stress-related activities can enlarge blood vessels around the eyes.
Managing stress through regular exercise, mindfulness practices (meditation, yoga), adequate sleep, and a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and reducing the appearance of dark circles.
Comprehensive Strategies to Control and Cure Under-Eye Dark Circles
Controlling and potentially reducing the appearance of under-eye dark circles involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses the underlying causes. Here’s a comprehensive strategy:
- Improve Sleep Habits: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep schedule to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress hormones.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Drink plenty of water throughout the day (at least 8 glasses). Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Include iron-rich foods to combat potential anemia.
- Skincare Routine: Use a gentle, hydrating eye cream with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, vitamin C, or retinol. Always protect your skin from the sun with a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher sunscreen.
- Treat Allergies: If allergies contribute to your dark circles, use antihistamines as needed and avoid known allergens.
- Eye Care: Take regular breaks from screens to reduce eye strain. Use artificial tears if your eyes feel dry.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can worsen dark circles. Reduce salt intake to minimize fluid retention.
- Home Remedies: Apply cool compresses or chilled cucumber slices to the under-eye area to constrict blood vessels. Cooled tea bags (especially green tea or chamomile) can also help reduce inflammation.
- Medical Treatments: Consult a dermatologist for options like chemical peels, laser therapy, or dermal fillers if dark circles are persistent and severe. Consider iron supplements *only* if diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia by a doctor.
Implementing these strategies consistently can significantly reduce the appearance of dark circles over time. However, persistent or worsening dark circles warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Get Personalized AdviceMelatonin Supplementation
Melatonin supplementation primarily helps regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality. Since poor sleep is a common contributing factor to dark circles, improving sleep through melatonin *can indirectly* help reduce their appearance. However, it is *not* a direct treatment for dark circles. Melatonin is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, stress management, and good skincare practices. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting melatonin supplementation, as it can interact with certain medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
Effects of Crying on Under-Eye Pigmentation
Excessive and recurrent crying can contribute to under-eye pigmentation and puffiness through several mechanisms:
- Vascular Changes: Crying causes the blood vessels around the eyes to expand, leading to a darker appearance.
- Skin Irritation: Frequent wiping or rubbing of the eyes can irritate the delicate skin, potentially leading to inflammation and hyperpigmentation over time.
- Fluid Retention: Crying can lead to temporary fluid retention and puffiness around the eyes.
To mitigate these effects:
- Avoid rubbing your eyes; gently pat them dry instead.
- Use a soft cloth or tissue.
- Apply a cool compress to the area to constrict blood vessels.
- Stay hydrated to help flush out excess fluids.
- Use a soothing eye cream to reduce irritation.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can effectively combat dark circles and under-eye pigmentation, achieving a healthier and more radiant complexion.
Are you struggling with dark circles and under-eye pigmentation? Achieve radiant, healthy skin through personalized nutrition plans designed by Dr. Sumaiya. With over 14 years of experience, Dr. Sumaiya Petiwala offers expert guidance on improving skin health from the inside out.
Contact Dr. Sumaiya’s NutriCare Today!Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What specific dietary changes can help reduce under-eye pigmentation caused by iron-deficiency anemia?
Focus on incorporating iron-rich foods into your diet, such as lean meats, leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), legumes (lentils, beans), nuts and seeds, and fortified foods (cereals, bread). Pairing these iron-rich foods with vitamin C-rich foods (citrus fruits, bell peppers) enhances iron absorption.
Q2: How can regular exercise contribute to the reduction of dark circles and overall skin health?
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for skin health. It improves blood circulation, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to skin cells. Exercise also helps reduce stress, which can exacerbate dark circles. Furthermore, it promotes detoxification through sweating and stimulates collagen production, contributing to firmer, healthier skin.
Q3: What are some advanced dermatological treatments available for persistent under-eye pigmentation?
For persistent and severe under-eye pigmentation, several advanced dermatological treatments are available. These include chemical peels (to exfoliate and lighten the skin), laser therapy (to target melanin and stimulate collagen), dermal fillers (to add volume and reduce the appearance of hollows), microneedling (to stimulate collagen and improve skin texture), topical treatments (prescription creams containing retinoids or hydroquinone), and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy (to promote tissue regeneration).
References
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): https://www.nih.gov/
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD): https://www.aad.org/